티스토리 뷰
요즘 챌린지 때 AR을 다루고 있다. 가장 핵심이 되는 피쳐 중 하나는 실제 현실에서 수직 평면을 감지해 포스트잇 같은 얇은 두께의 "카드 형태의 박스"를 붙이는 작업이었다. 급하게 ARKit과 RealityKit을 공부하다보니 놓치는게 많았다. 공부하며 작업하며 헤매던 부분을 기록해본다.
ARView
ARView는 RealityKit을 통해 AR 경험을 제공할 수 있는 UIKit 뷰이다. 그렇기 때문에 RealityKit 뿐 아니라 ARKit에도 의존한다. 예컨대 ARSession 타입의 session 프로퍼티와, RealityKit의 Scene 타입인 scene 프로퍼티를 같이 가진다. ARView를 초기화하면 각 프로퍼티가 각 타입 인스턴스로 주입되어 제공된다. 대부분 session(ARSession)을 설정하고 시작한 뒤에, 현실을 증강하는 엔티티를 scene(Scene)에 추가하는 흐름으로 진행한다.
ARAnchor와 AnchorEntity는 다르다
덕분에 ARKit과 RealityKit을 적절히 학습해야 AR 경험을 잘 만들어낼 수 있다. 평면을 감지하는 것은 ARKit의 책임이다. ARSession을 시작할 때 Configuration을 ARWorldConfiguraion 등으로 지정하고, planeDetection 옵션을 추가하면 ARSession 시작 후 평면을 감지한다. ARSession은 평면 감지 뿐 아니라 모션 트래킹, 카메라 패스쓰루, 이미지 분석 등 AR 경험을 위한 주요 태스크를 전담하는 객체이다.
class CustomARView: ARView {
required init(frame frameRect: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frameRect)
setup()
}
required init?(coder decoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
private func setup() {
self.environment.sceneUnderstanding.options.insert(.occlusion)
self.environment.sceneUnderstanding.options.insert(.receivesLighting)
self.session.delegate = self
resetSession()
}
func resetSession(initialWorldMap: ARWorldMap? = nil) {
let configuration = ARWorldTrackingConfiguration()
configuration.planeDetection = [.vertical] // 수직 평면 감지
configuration.sceneReconstruction = .meshWithClassification
// self.debugOptions = [
// .showAnchorGeometry,
// .showFeaturePoints,
// .showWorldOrigin,
// .showPhysics,
// ]
self.session.run(configuration)
}
}
ARKit은 CV 기술과 LiDAR를 통해 감지한 현실의 대상을 ARAnchor 타입으로 표현한다. 평면을 감지하는 경우 하위 타입인 ARPlaneAnchor로 표현된다. 새로 감지한 앵커나 기존 앵커의 업데이트는 ARSessionDelegate를 채택하는 클래스 인스턴스를 ARSession의 delegate 프로퍼티에 할당하면 위임받을 수 있다.
extension CustomARView: ARSessionDelegate {
/// MARK: 앵커가 추가되었을 때
func session(_ session: ARSession, didAdd anchors: [ARAnchor]) {
anchors.compactMap { $0 as? ARPlaneAnchor }
.forEach { planeAnchor in
let center = planeAnchor.center // simd_float3 (x, 0, z)
let extent = planeAnchor.planeExtent // ARPlaneExtent
print("Added ARPlaneAnchor: center(\(center)), extent(\(extent))")
visualizePlaneAnchor(planeAnchor)
}
}
/// MARK: 앵커가 업데이트되었을 때
func session(_ session: ARSession, didUpdate anchors: [ARAnchor]) {
anchors.compactMap { $0 as? ARPlaneAnchor }
.forEach { planeAnchor in
let center = planeAnchor.center // simd_float3 (x, 0, z)
let extent = planeAnchor.planeExtent // ARPlaneExtent
print("Changed ARPlaneAnchor: center(\(center)), extent(\(extent))")
removePreviousPlaneAnchorVisualize(planeAnchor)
visualizePlaneAnchor(planeAnchor)
}
}
// MARK: - visualizePlaneAnchor(_:ARPlaneAnchor) 생략
// MARK: - removePreviousPlaneAnchorVisualize(_:ARPlaneAnchor) 생략
}
이때 ARAnchor는 RealityKit의 AnchorEntity와는 다르다. 앞에서 말했듯, ARAnchor는 ARSession에서 감지한 현실 세계의 대상의 좌표와 회전을 표현한다. 반면에 AnchorEntity는 Scene에 렌더링되는 요소를 표현하는 Entity의 하위 타입이다. Scene에 고정되어 다른 자식 엔티티 위치의 기준 점이 된다.
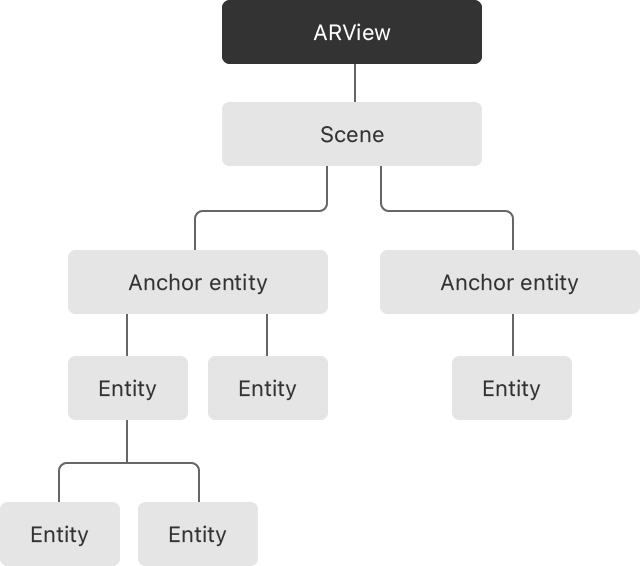
AnchorEntity는 아래와 같이 RealityKit이 적절한 곳에 배치하도록 맡길 수도 있다. QuickLook과 같이 간단한 엔티티를 카메라 근처 평면에 띄우고 싶다면 이것으로도 충분할 것이다.
/// see: https://developer.apple.com/documentation/realitykit/anchorentity/init(_:)-9rdwu
AnchorEntity(.plane(.horizontal,
classification: .any,
minimumBounds: SIMD2<Float>(0.2, 0.2)
))
다만 이번 챌린지에서는 모든 스캔된 평면에 대해 일일히 카드 엔티티를 붙이는 기능을 필요로 했기 때문에 ARKit로부터 얻는 ARAnchor를 가지고 직접 AnchorEntity를 만들 수 있어야 했다. 아래 코드는 ARAnchor로부터 AnchorEntity를 얻고 그 자식으로 인식한 평면의 윤곽을 그리는 ModelEntity들을 추가해 씬에 렌더링한다.
/// see: https://developer.apple.com/documentation/realitykit/anchorentity/init(anchor:)
func visualizePlaneAnchor(_ planeAnchor: ARPlaneAnchor) {
// MARK: - 평면을 그린다.
// 테두리용 재질
var borderMaterial = UnlitMaterial()
borderMaterial.color = .init(tint: .green)
let frameThickness: Float = 0.005
let width = planeAnchor.planeExtent.width
let height = planeAnchor.planeExtent.height
// 평면의 방향에 따라 박스 크기와 방향 결정
var topFrameSize: SIMD3<Float>
var bottomFrameSize: SIMD3<Float>
var leftFrameSize: SIMD3<Float>
var rightFrameSize: SIMD3<Float>
if planeAnchor.alignment == .vertical {
// 수직 평면 (벽) - Z축이 높이가 됨
topFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(width, 0.01, frameThickness)
bottomFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(width, 0.01, frameThickness)
leftFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(frameThickness, 0.01, height)
rightFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(frameThickness, 0.01, height)
} else {
// 수평 평면 (바닥/천장) - Y축이 높이가 됨
topFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(width, frameThickness, 0.01)
bottomFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(width, frameThickness, 0.01)
leftFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(frameThickness, height, 0.01)
rightFrameSize = SIMD3<Float>(frameThickness, height, 0.01)
}
// 테두리 프레임 생성
let topFrame = ModelEntity(mesh: MeshResource.generateBox(size: topFrameSize), materials: [borderMaterial])
let bottomFrame = ModelEntity(mesh: MeshResource.generateBox(size: bottomFrameSize), materials: [borderMaterial])
let leftFrame = ModelEntity(mesh: MeshResource.generateBox(size: leftFrameSize), materials: [borderMaterial])
let rightFrame = ModelEntity(mesh: MeshResource.generateBox(size: rightFrameSize), materials: [borderMaterial])
// 프레임 위치 설정
if planeAnchor.alignment == .vertical {
// 수직 평면일 때의 위치
topFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(0, 0, height/2 - frameThickness/2)
bottomFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(0, 0, -height/2 + frameThickness/2)
leftFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(-width/2 + frameThickness/2, 0, 0)
rightFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(width/2 - frameThickness/2, 0, 0)
} else {
// 수평 평면일 때의 위치
topFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(0, height/2 - frameThickness/2, 0)
bottomFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(0, -height/2 + frameThickness/2, 0)
leftFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(-width/2 + frameThickness/2, 0, 0)
rightFrame.transform.translation = SIMD3<Float>(width/2 - frameThickness/2, 0, 0)
}
// AnchorEntity 생성 및 평면 앵커에 연결
let anchorEntity = AnchorEntity(anchor: planeAnchor)
// 프레임들을 앵커에 추가
anchorEntity.addChild(topFrame)
anchorEntity.addChild(bottomFrame)
anchorEntity.addChild(leftFrame)
anchorEntity.addChild(rightFrame)
anchorEntity.components[DetectedPlaneComponent.self] = DetectedPlaneComponent()
// ARView에 추가
self.scene.addAnchor(anchorEntity)
}
HasAnchoring은 Anchor 역할을 할 엔티티를 정의할 때 쓴다
다음으로 헤맸던 부분은 벽에 카드 엔티티를 붙이는 기능을 만들어두고, 리팩토링하다가 맞닥드렸다. 원래는 카드 형태 ModelEntity를 다음과 같은 메서드로 직접 생성했다.
func createCardEntity() -> ModelEntity {
let boxMesh = MeshResource.generateBox(size: [postItSize, postItHeight, postItSize]) // 50cm x 1cm x 50cm
let material = SimpleMaterial(color: .red, isMetallic: false)
let modelEntity = ModelEntity(mesh: boxMesh, materials: [material])
modelEntity.components[LearningCardComponent.self] = LearningCardComponent()
modelEntity.generateCollisionShapes(recursive: true)
let beginEventSub = self.scene.subscribe(
to: CollisionEvents.Began.self,
on: modelEntity
) { [weak self] event in
// 충돌이 감지되면 한 쪽 엔티티를 제거한다
print("collision started")
event.entityB.removeFromParent()
self?.collisionSubscriptions.removeValue(forKey: event.entityB)
GameManager.instance.cardDetached()
if GameManager.instance.currentMode != .ready
&& GameManager.instance.attachedCardsCount < GameManager.instance.totalCardCount ?? 15 {
self?.attachToPlane()
}
}
collisionSubscriptions[modelEntity] = beginEventSub
return modelEntity
}
아주 잘됐다. 그러다 이걸 별도의 커스텀 엔티티로 만들고 싶어서 다음과 같이 Entity를 상속하는 CardEntity를 정의하고, 위의 메서드를 호출하는 대신 CardEntity 인스턴스를 생성했다. ModelEntity는 직접 상속이 불가능하다. 다른 모듈에 존재하는 클래스는 접근제어자가 open이어야 상속 가능한데 이건 public이다. (아마 HasModel, HasCollision, HasAnchoring 등의 프로토콜이 존재하는 이유일 것이다.)
class CardEntity: Entity, HasModel, HasCollision, HasAnchoring {
static let postItSize: Float = 0.2
static let postItDepth: Float = 0.01
/// Used to keeping a reference of any subscriptions involving this entity
var entitySubs: [Cancellable] = []
required init(color: UIColor) {
super.init()
// Shape of this entity for any collisions including gestures
self.components[CollisionComponent.self] = CollisionComponent(
shapes: [.generateBox(size: [CardEntity.postItSize, CardEntity.postItDepth, CardEntity.postItSize])],
mode: .trigger,
filter: .sensor
)
// Model of this entity, the physical appearance is a 1x0.2x1 cuboid
self.components[ModelComponent.self] = ModelComponent(
mesh: .generateBox(size: [CardEntity.postItSize, CardEntity.postItDepth, CardEntity.postItSize]),
materials: [SimpleMaterial(
color: color,
isMetallic: false)
]
)
self.components[LearningCardComponent.self] = LearningCardComponent()
}
convenience init(color: UIColor, position: SIMD3<Float>) {
self.init(color: color)
self.position = position
}
required convenience init() {
self.init(color: .orange)
}
}
이렇게 했더니 카드가 인식한 평면과는 전혀 상관 없는 위치에 배치됐다. 삽질을 계속했는데, 결국 HasAnchoring을 채택한 것이 문제였다. 카드 엔티티가 HasAnchoring을 채택했기에 AnchorEntity처럼 기능하게 된다. 이로 인해 평면의 ARAnchor로 생성했던 AnchorEntity의 자식으로 또 다시 AnchorEntity가 배치된 격이 된 것이다. AnchorEntity의 문서를 보면 그런 계층 관계가 아주 불가능한 것은 아닌 것 같지만, 자연스러운 관계는 아니다.

AnchorEntity, HasAnchoring에 대한 이해가 부족해서 헤맸던 것이었고, HasAnchoring을 제외했더니 문제 없이 잘 동작했다.
참고자료
https://developer.apple.com/kr/videos/play/wwdc2019/603
Introducing RealityKit and Reality Composer - WWDC19 - 비디오 - Apple Developer
Architected for AR, RealityKit provides developers access to world-class capabilities for rendering, animation, physics, and spatial...
developer.apple.com
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/arkit
ARKit | Apple Developer Documentation
Integrate hardware sensing features to produce augmented reality apps and games.
developer.apple.com
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/realitykit
RealityKit | Apple Developer Documentation
Simulate and render 3D content for use in your augmented reality apps.
developer.apple.com
'컴퓨터 > iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [iOS] 좌표로 주소 얻기 - CLGeocoder를 이용한 역지오코딩 (1) | 2025.03.04 |
|---|---|
| 스위프트 테스팅 소개 (Meet Swift Testing, WWDC24) (0) | 2025.02.02 |
| Xcode 에디터 수평분할, 수직분할 (0) | 2025.02.02 |
| [iOS] 날짜/시간 치트시트 (0) | 2025.01.15 |
| [iOS] CoreData 사용해보기 (0) | 2024.12.24 |
